If your achilles hurts, then this article is for you. Experiencing pain in the back of your heel can be quite distressing, particularly when it affects your daily activities. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that many individuals face, especially those who are active in sports or engage in activities involving running and jumping. Understanding the intricacies of this condition can help manage symptoms and prevent further complications. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments available for Achilles tendinitis, as well as strategies to manage and prevent this painful condition.
FAQ
How to fix a sore Achilles?
If you’re dealing with a sore Achilles, you might want to start by resting the affected leg to reduce stress on the Achilles tendon. Applying ice to the back of your ankle can help in reducing inflammation and provide pain relief. Over-the-counter pain medications may also help in managing the discomfort. Stretching exercises that target the calf muscle and the tendon in the body can promote healing and prevent further damage. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to tailor a treatment plan specific to your needs, especially if the pain persists.
Does walking help Achilles tendonitis?
Walking can be beneficial for those suffering from mild Achilles tendonitis, as it keeps the tendon mobile and prevents stiffness. However, it is crucial to walk on even surfaces and wear supportive footwear to avoid further strain. It’s essential to listen to your body and stop if the activity causes pain. Gradually increasing your walking intensity under the guidance of a sports medicine specialist can help strengthen the tendon without exacerbating inflammation. Always consult with a healthcare provider to ensure walking is appropriate for your stage of recovery.
Can Achilles tendonitis go away on its own?
Achilles tendonitis can sometimes resolve on its own with rest and proper care. Avoiding activities that cause pain and allowing the tendon time to heal is crucial. However, without proper management, the condition can become chronic and lead to more severe issues like tendon rupture. Implementing lifestyle changes and engaging in rehabilitation exercises can expedite recovery and prevent recurrence. Consulting with a healthcare professional ensures that you’re on the right track to recovery and helps address any underlying issues promptly.
Should I stretch my Achilles tendon if it hurts?
Stretching the Achilles tendon can be a double-edged sword. While gentle stretching can alleviate tightness and improve flexibility, overstretching can exacerbate tendon damage. It’s important to perform stretches that are specifically designed for tendon injuries and to do so under the guidance of a physical therapist. They can demonstrate techniques that target the calf muscle and Achilles tendon safely. If stretching causes increased pain, it’s crucial to stop and seek advice from a medical professional to avoid further injury.
What is Achilles Tendinitis?
How is Achilles Tendinitis Defined?
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, the strongest tendon in the body that connects your calf muscle to your heel bone. It occurs when the tendon becomes inflamed, often due to repetitive stress from activities like running and jumping. The inflammation leads to tendon pain and stiffness, particularly noticeable at the back of the ankle. This condition can affect anyone but is most common in athletes and those who increase their activity levels abruptly without proper conditioning.
What are the Types of Achilles Tendinitis?
Achilles tendinitis can be categorized into two main types: insertional and noninsertional. Insertional Achilles tendinitis affects the lower part of the tendon where it connects to the heel bone, while noninsertional Achilles tendinitis involves the fibers in the middle portion of the tendon. Both types of Achilles tendinitis can cause pain and swelling, but they may require different treatment approaches. Understanding the type of Achilles tendinitis you have is crucial for effective management and recovery.
What Causes Achilles Tendinitis?
Several factors can contribute to the development of Achilles tendinitis. Overuse from frequent running and jumping is a common cause, especially without adequate preparation or warm-up. Other causes include a sudden increase in physical activity, wearing improper footwear, or a tight calf muscle that adds stress to the tendon. Biomechanical issues, such as flat feet or a naturally high arch, can also increase the risk for Achilles tendon injuries. Identifying the underlying causes is essential for preventing recurrence and promoting long-term tendon health.
Recognizing the Symptoms
What are the Common Symptoms of Achilles Tendinitis?
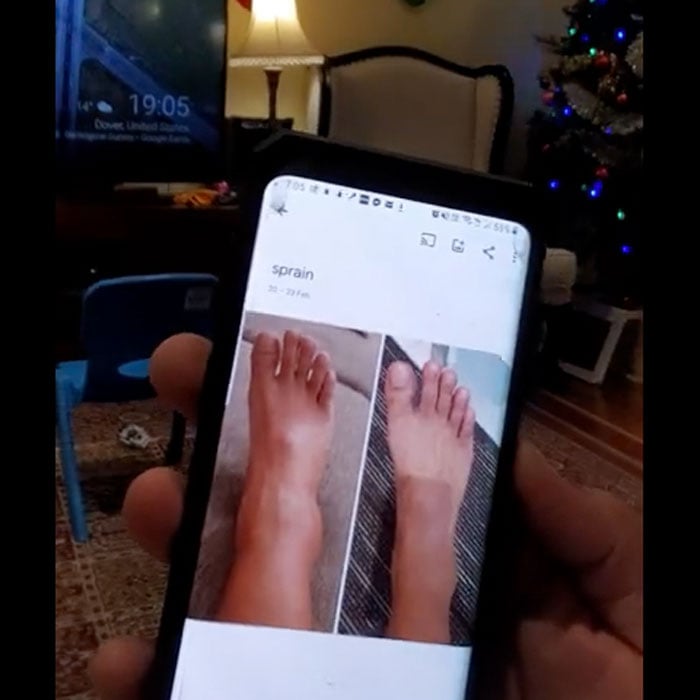
Common symptoms of Achilles tendinitis include pain and stiffness in the back of the ankle, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking in the morning. Swelling along the tendon or at the heel may be noticeable, and the area might be tender to the touch. You might also experience a limited range of motion and difficulty standing on tiptoe. Early recognition of these symptoms is important to prevent the condition from progressing to more severe tendon injuries.
How Can You Differentiate Between Tendinitis and Other Conditions?
Differentiating Achilles tendinitis from other conditions, such as an Achilles tendon rupture or bursitis, can be challenging. Tendonitis typically presents with gradual onset of pain and can be linked to recent increases in activity levels. In contrast, a tendon rupture often results in sudden, severe pain and an inability to bear weight. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for an accurate diagnosis, as they can conduct physical examinations and imaging tests to confirm the condition.
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
Seeking medical attention is crucial if you experience persistent pain that does not improve with rest, swelling, or if you suspect a tendon rupture. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote faster recovery. If you experience a sudden sharp pain or hear a popping sound in the back of your ankle, it’s imperative to seek immediate medical care, as these are signs of an Achilles tendon rupture. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnosing Achilles Tendinitis
What Tests are Used to Diagnose Achilles Tendinitis?
Diagnosing Achilles tendinitis typically involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging tests. A healthcare provider will assess the range of motion and look for signs of inflammation or tenderness. Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI can provide detailed images of the tendon and surrounding structures, helping to identify the extent of tendon damage and rule out other conditions like tendon rupture. These tests are crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment.
What Should You Expect During a Doctor’s Visit?
During a doctor’s visit for Achilles tendinitis, you can expect a thorough examination of the foot and ankle. The healthcare provider will discuss your symptoms, activity level, and any recent changes in your routine that may have contributed to the condition. They may perform specific tests to evaluate the strength and flexibility of the tendon. Based on the findings, they will recommend a treatment plan tailored to your needs, which may include rest, medication, physical therapy, or further diagnostic testing.
How is the Severity of the Condition Assessed?
The severity of Achilles tendinitis is assessed based on symptom intensity, functional limitations, and imaging results. Mild cases may present with occasional pain that subsides with rest, while severe cases can involve constant pain and significant impairment. Imaging tests can reveal the extent of tendon inflammation and any structural changes. Understanding the severity helps in formulating an effective treatment plan and setting realistic recovery expectations.
Treatment Options Available
What are the Non-Surgical Treatment Options?
Non-surgical treatment options for Achilles tendinitis focus on reducing pain and inflammation while promoting healing. Resting the affected leg and applying ice can alleviate symptoms. Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the calf muscle and improve flexibility of the tendon. Orthotic devices or heel lifts may be recommended to reduce stress on the tendon. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also be used to manage pain and inflammation. These treatments are often effective in resolving symptoms without the need for surgical intervention.
When is Surgery Considered Necessary?
Surgery for Achilles tendinitis is considered when non-surgical treatments fail to alleviate symptoms after several months. It may also be necessary if there is significant tendon damage or if a tendon rupture has occurred. Surgical procedures aim to remove damaged tissue, repair the tendon, and restore functionality. Recovery from surgery can be lengthy, requiring physical therapy to regain strength and mobility. Consulting with an orthopedic surgeon can help determine if surgery is the right option based on the severity and duration of the condition.
How Effective are Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation?
Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a crucial role in treating Achilles tendinitis. They focus on strengthening the calf muscle, improving range of motion, and promoting tendon healing. Tailored exercise programs can help prevent recurrence and address any biomechanical issues that may have contributed to the condition. The effectiveness of physical therapy depends on adherence to the prescribed regimen and the individual’s response to treatment. Regular follow-ups with a physical therapist ensure progress and allow for adjustments to the rehabilitation plan as needed.
Prevention and Management Strategies
How Can You Prevent Achilles Tendinitis?
Preventing Achilles tendinitis involves adopting practices that reduce stress on the tendon. Gradually increasing activity levels allows the tendon to adapt, reducing the risk of injury. Wearing supportive footwear and incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the calf muscle can enhance tendon resilience. Listening to your body’s signals and avoiding activities that cause pain are essential. Implementing these strategies can help maintain tendon health and prevent the onset of Achilles tendinitis.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage the Condition?
Managing Achilles tendinitis effectively involves making lifestyle changes that minimize pain and promote healing. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the load on the tendon, while incorporating low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can maintain fitness without exacerbating symptoms. Regularly stretching the calf muscle and Achilles tendon improves flexibility. Avoiding high-impact activities can prevent further tendon damage. Being mindful of your activity choices and making necessary adjustments can significantly improve your quality of life when living with Achilles tendinitis.
Are There Exercises to Strengthen the Achilles Tendon?
Exercises to strengthen the Achilles tendon are vital for recovery and prevention. Eccentric heel drops, where you lower your heel below the level of a step, are particularly effective in strengthening the tendon. Calf raises and seated calf stretches can also improve tendon strength and flexibility. It’s important to perform these exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist to ensure proper form and avoid injury. Regularly incorporating these exercises into your routine can fortify the tendon and reduce the risk of future injuries.
Living with Achilles Tendinitis
How Can You Adapt Daily Activities to Minimize Pain?
Adapting daily activities to minimize pain from Achilles tendinitis involves making thoughtful adjustments. Choosing supportive footwear with cushioned soles can alleviate stress on the tendon. Incorporating rest periods into your routine allows for recovery and reduces inflammation. Avoiding activities that require sudden changes in direction or high-impact movements can prevent exacerbating symptoms. Engaging in low-impact activities that encourage blood flow and maintain mobility can help manage pain and support the healing process.
What Support Systems are Available for Those Affected?
Support systems for individuals affected by Achilles tendinitis are crucial for recovery and emotional well-being. Physical therapists provide guidance on exercises and pain management strategies. Support groups and online communities offer a platform to share experiences and advice. Access to sports medicine specialists ensures expert care and personalized treatment plans. These resources provide valuable support and encouragement throughout the healing process, helping individuals navigate the challenges of living with Achilles tendinitis.
What is the Long-Term Outlook for Achilles Tendinitis Patients?
The long-term outlook for Achilles tendinitis patients is generally positive with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. Many individuals experience significant improvement in symptoms and can return to their usual activities. However, recurrence can occur if preventative measures are not maintained. Ongoing adherence to stretching and strengthening exercises, along with mindful activity choices, is essential for long-term tendon health. With the right approach, individuals can manage Achilles tendinitis effectively and enjoy an active lifestyle.